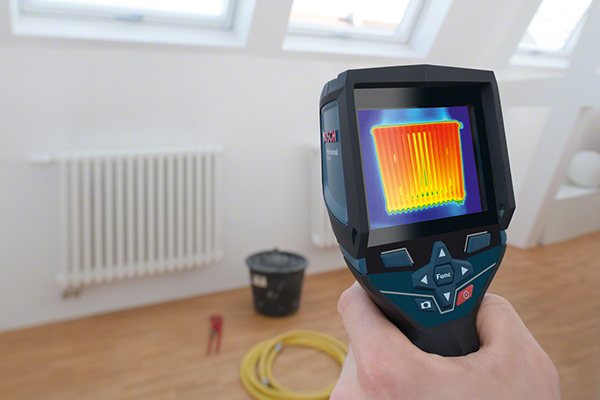
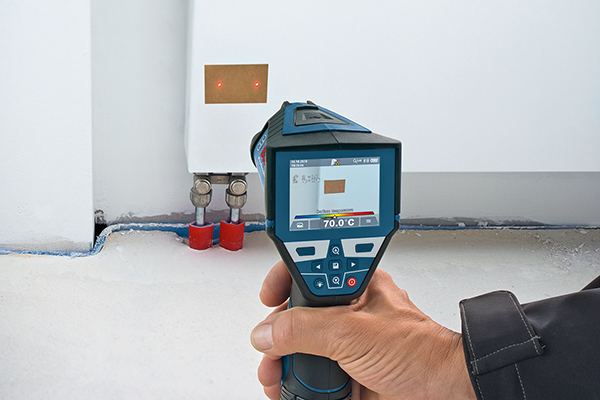
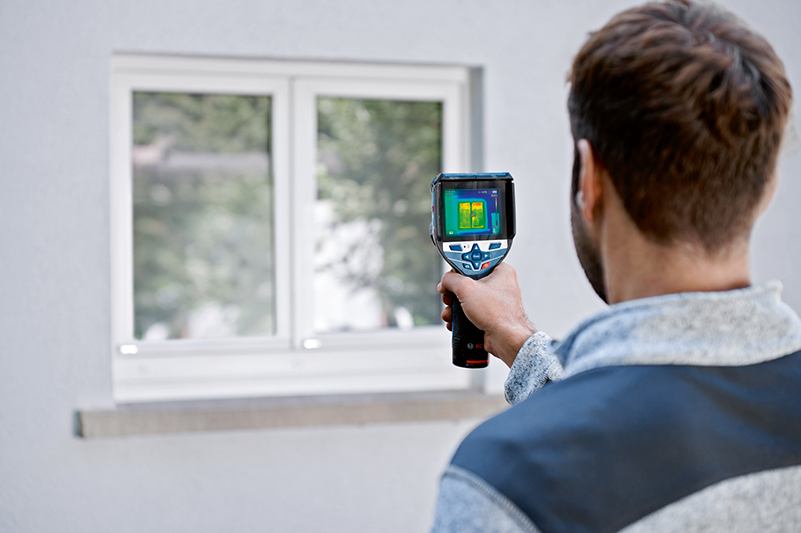
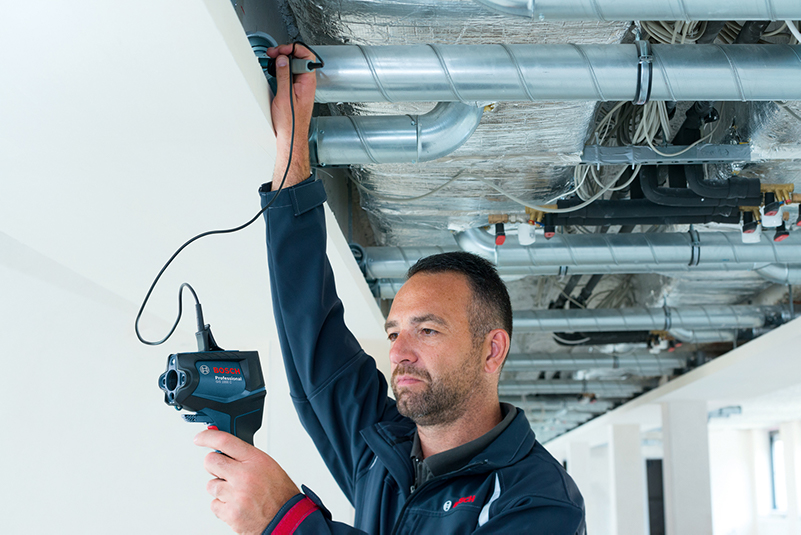
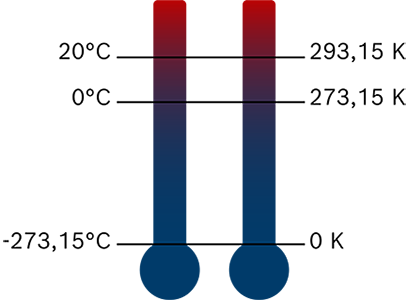
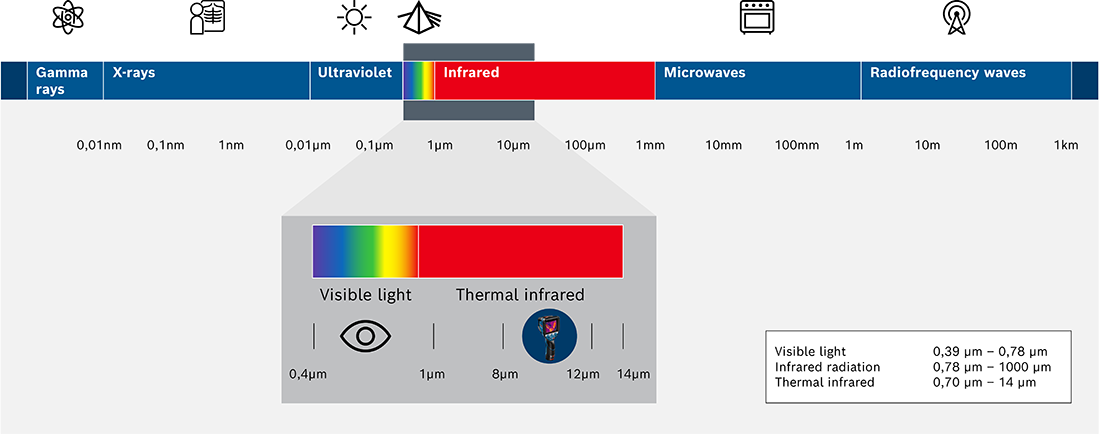
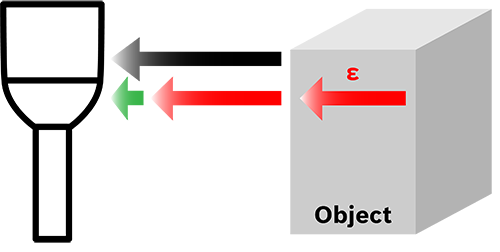
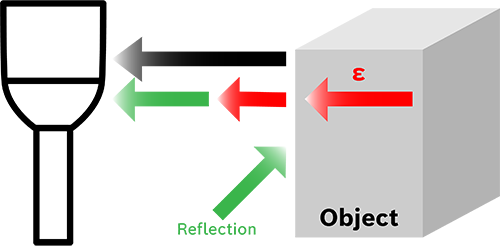
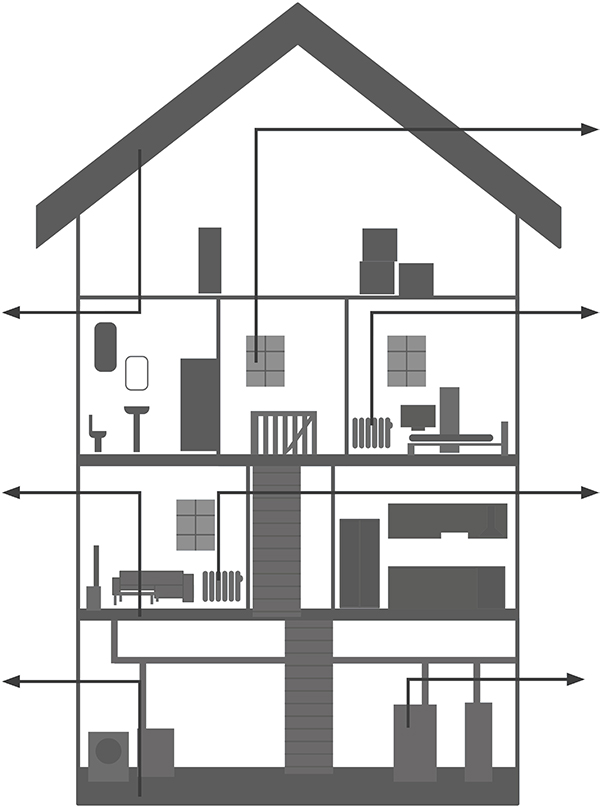
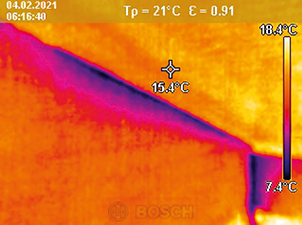
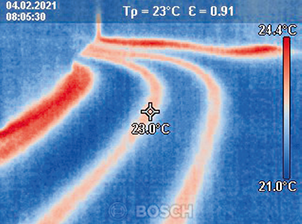
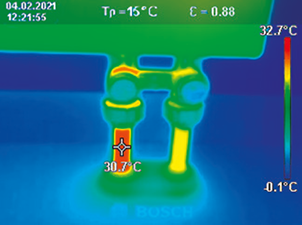
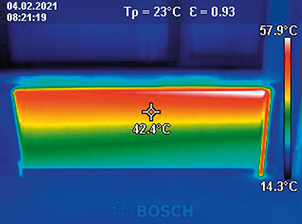
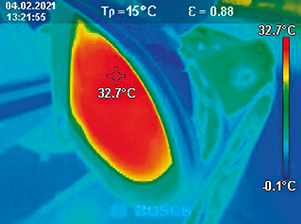
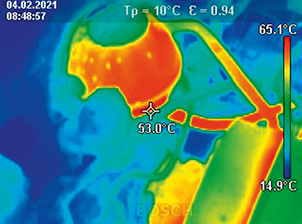
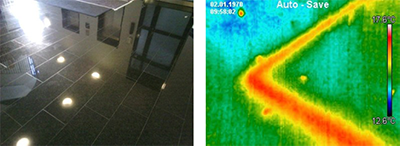
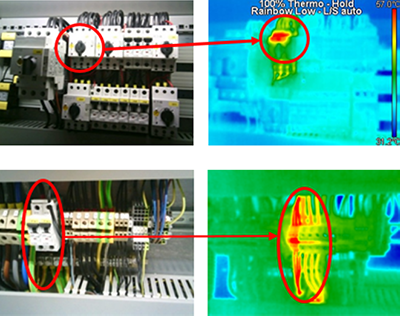
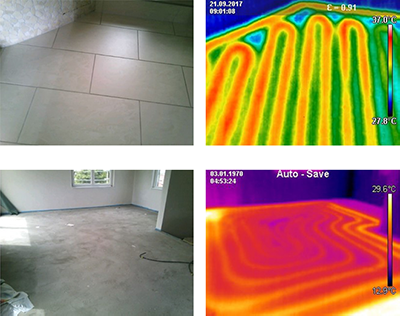
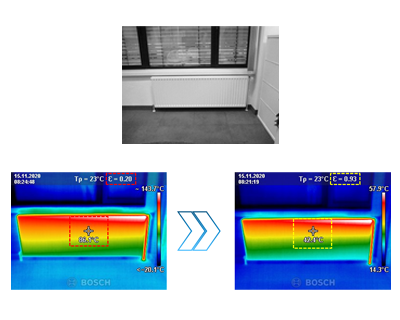
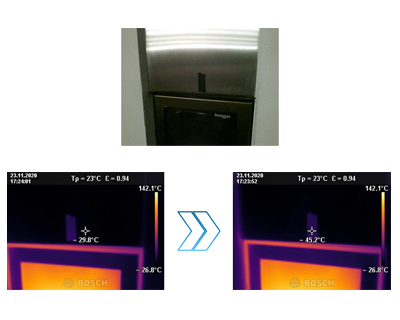
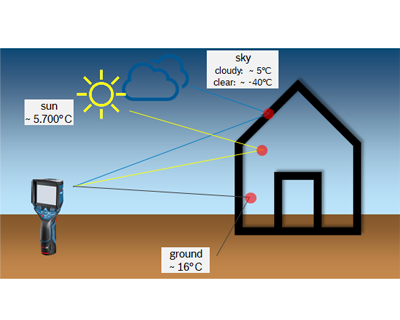
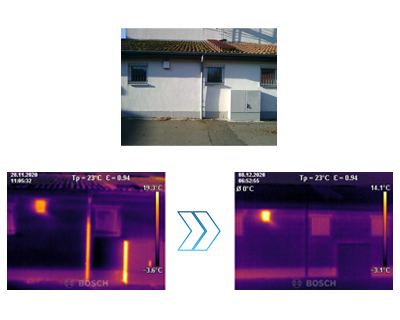
Advantages
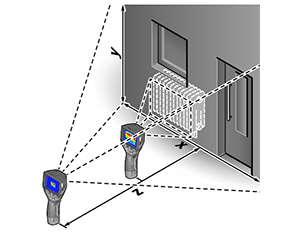
- Contact-free, therefore measuring is possible with objects that ...
- ... are resting and moving
- ... are heavily accessible
- ... are very hot and
- ... are current-carrying
- Non-reactive and destruction-free measuring
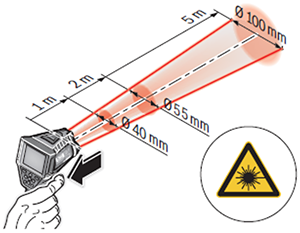
- Very short measuring time
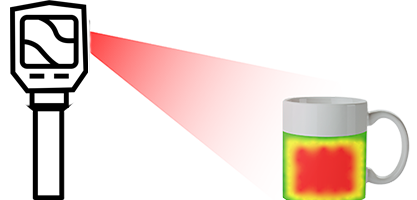
- Area-measured temperature information